Visual
Logo Design
Logos are usually the first thing a user sees and the last thing a user remembers. Therefore, a logo should represent the brand in an easy to understand way and be simple enough to reproduce on a variety of mediums.


Visual
Logo Design
Logos are usually the first thing a user sees and the last thing a user remembers. Therefore, a logo should represent the brand in an easy to understand way and be simple enough to reproduce on a variety of mediums.


Visual
Branding Design
Balancing a webpage is no easy task, but what is most important to a user can be prioritized using color, typography, size, distance, and shape.

Visual
App Screen Design
While desktops have the luxury of space, phone and tablet sizing often means focusing on one task at a time. When I design for apps, I focus heavily on visual design and flow diagramming.
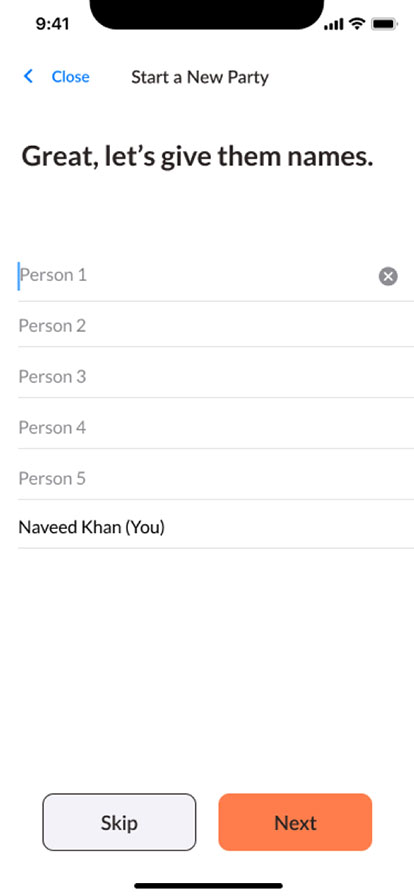
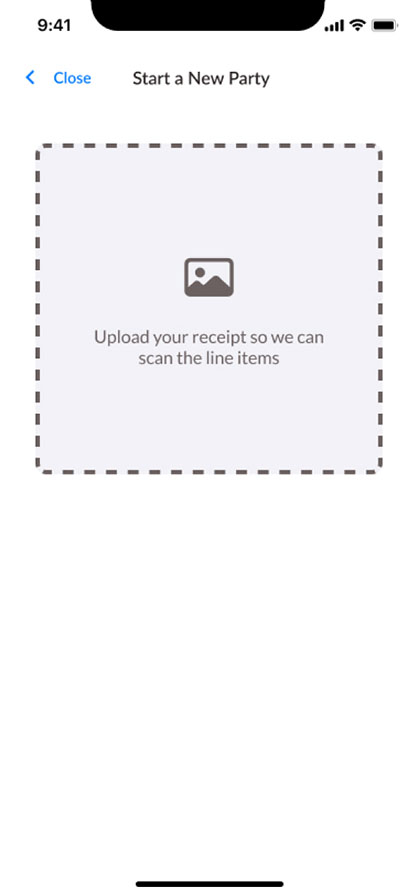


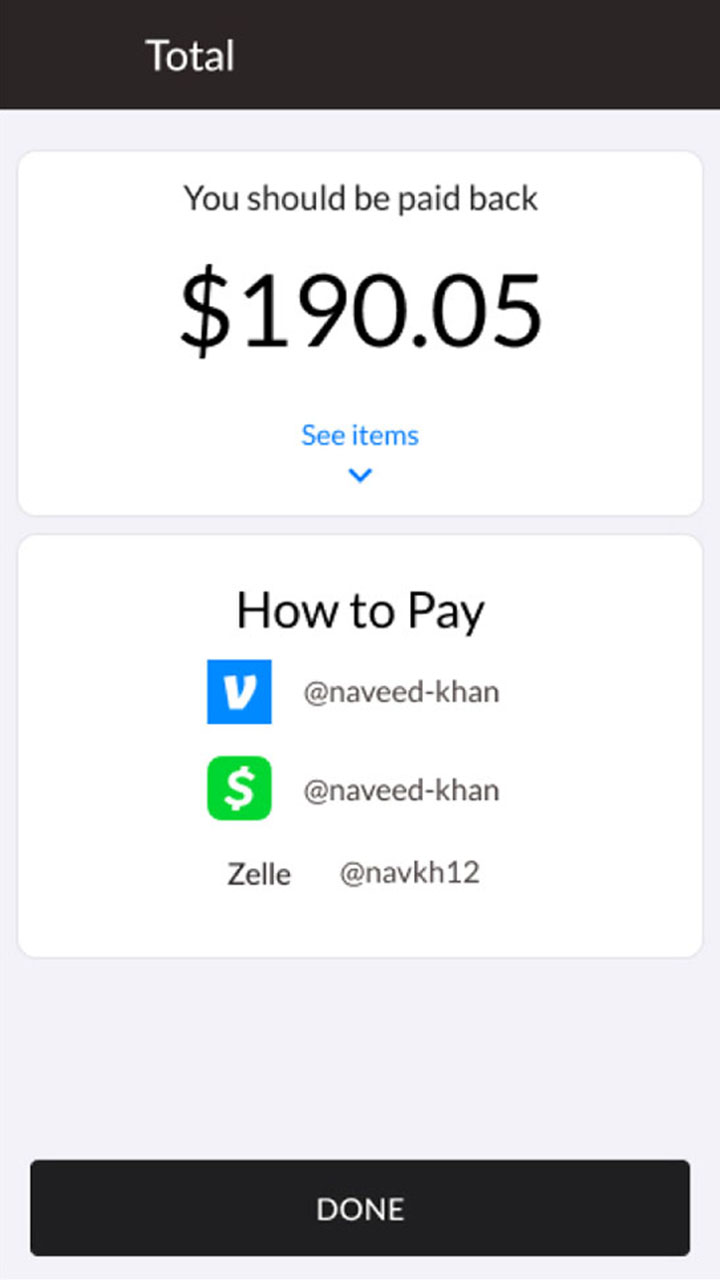
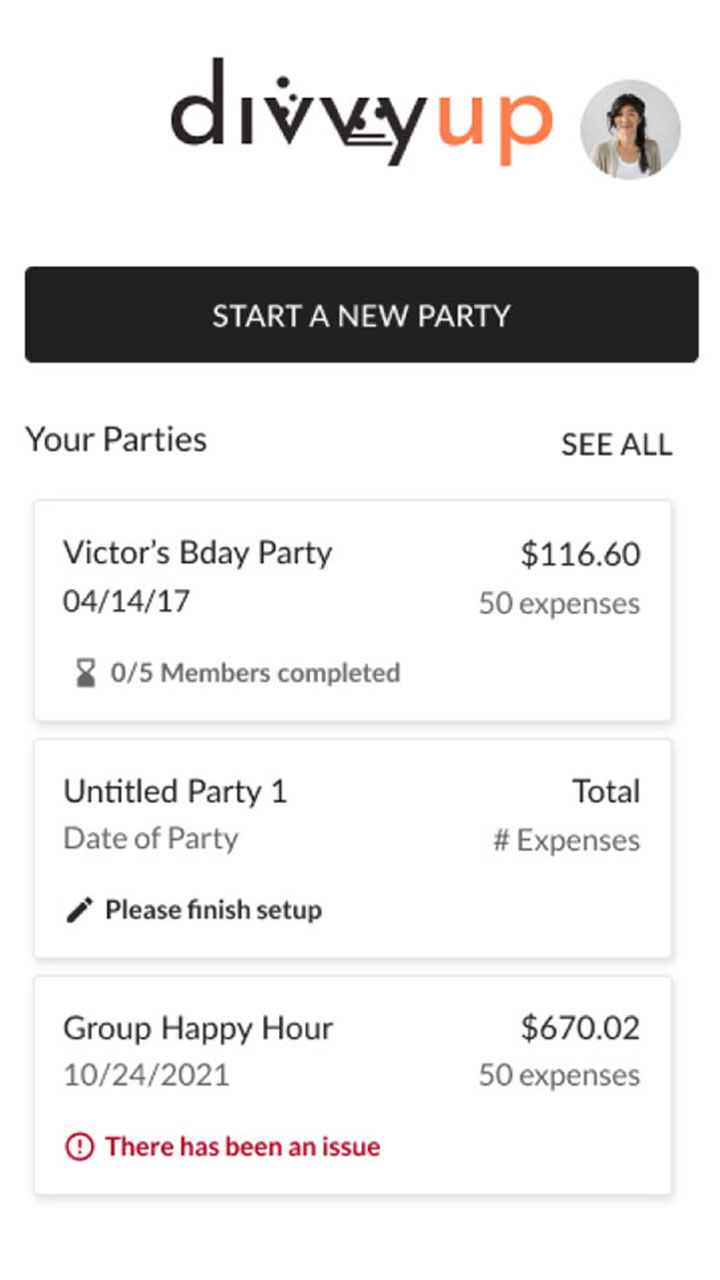
Visual
Web Screen Design
The UX industry focuses on ‘mobile-first’ design. However, I have worked on web applications that will never be used on mobile, and don’t have the resources to optimize at all screen sizes. When this happens, I do research into the most common browser size for our users, use that as a starting point, and make sure it is adjustable at various breakpoints.
Visual
Design Systems
While designing from a blank canvas can be fun, it ends up being taxing for both the designer and the developer. When working long term on a project, I prefer to invest in creating a robust, reusable design system or relying on an open source design system.
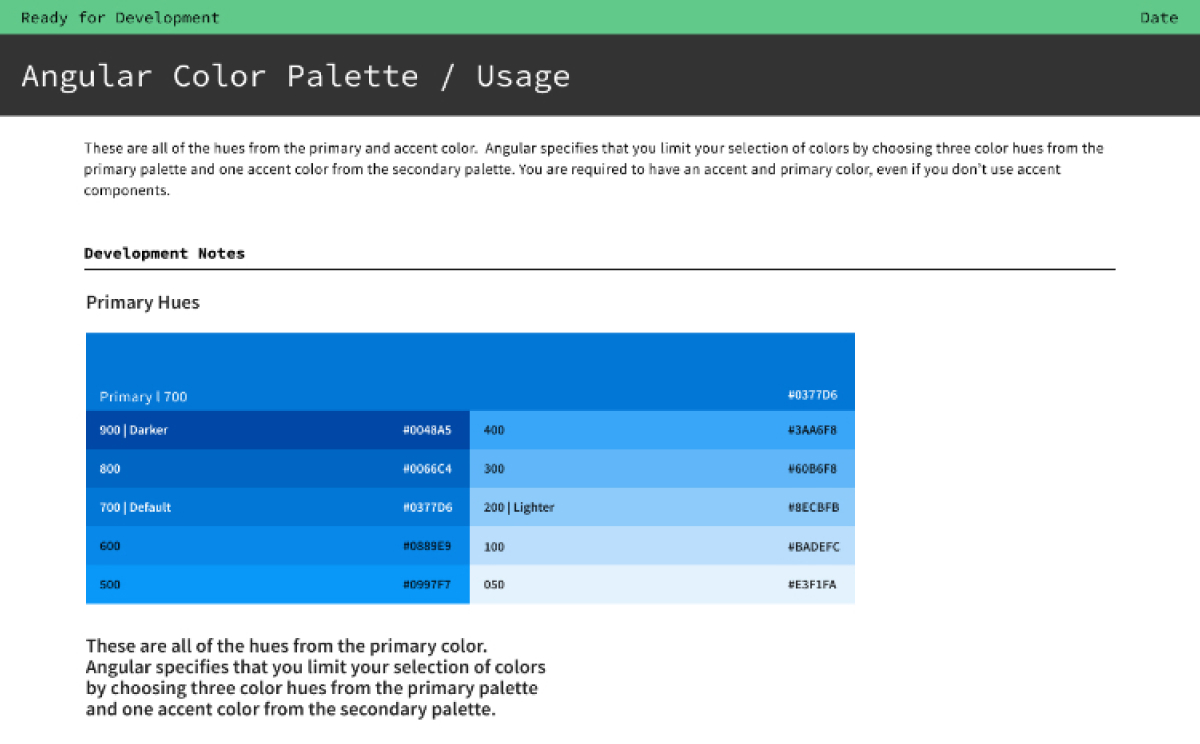
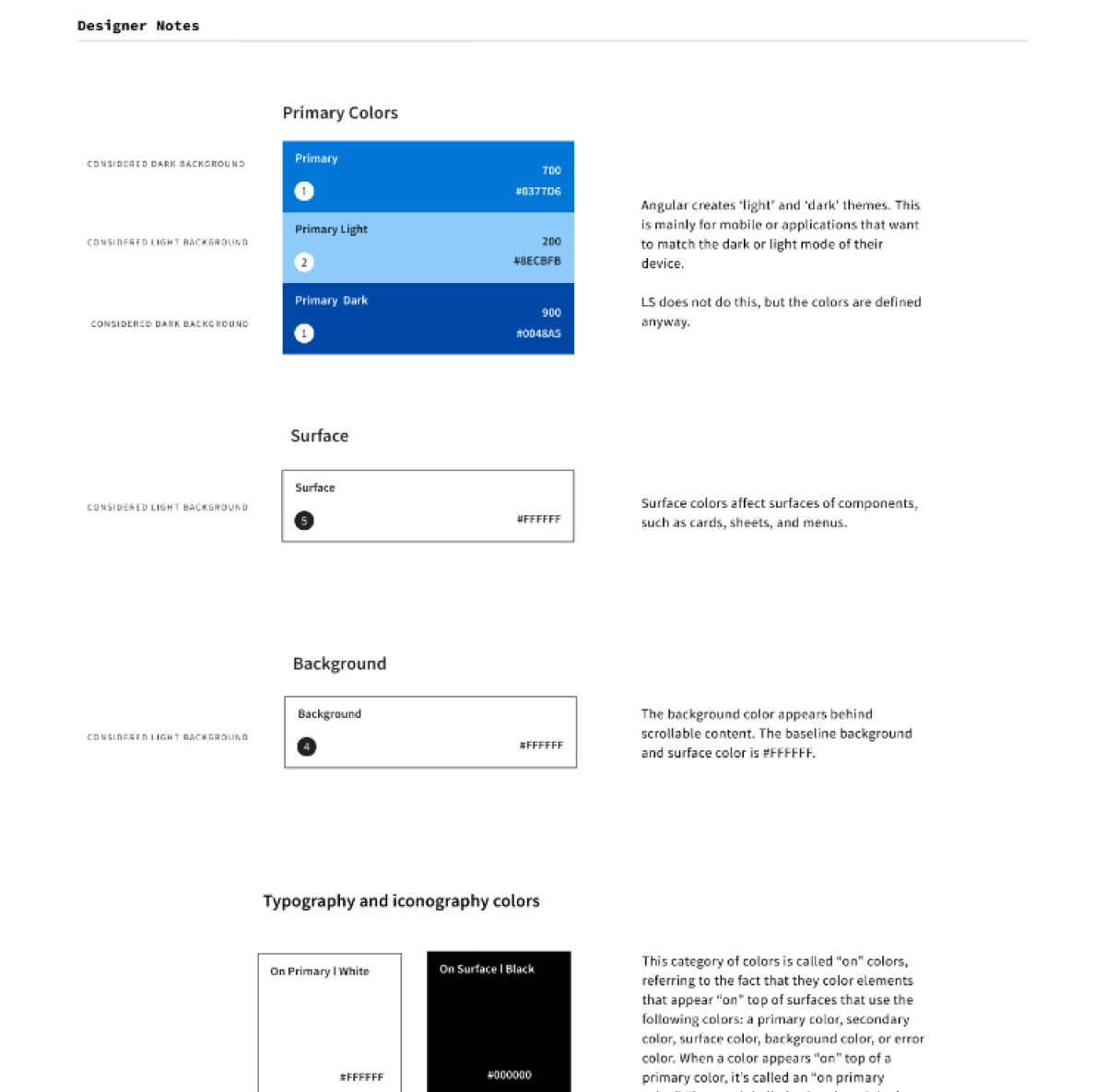

Visual
Interaction Design
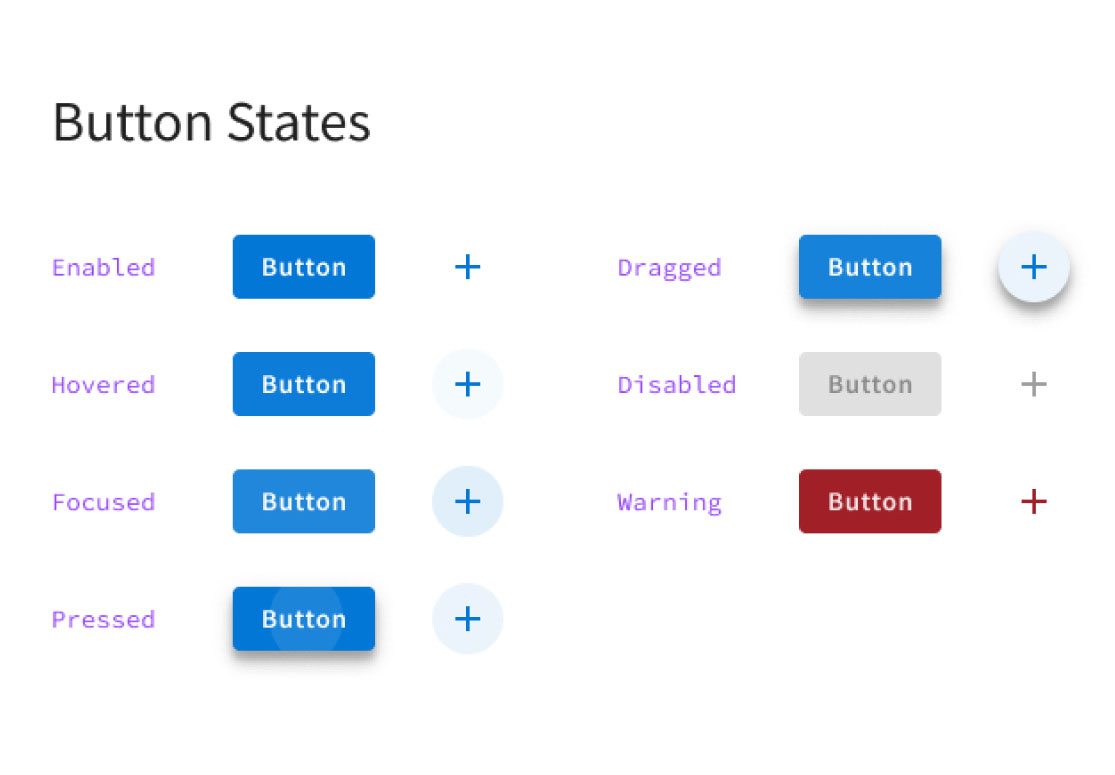
Some of the most delightful parts of digital experiences are the interactions. Alternatively, there is nothing more frustrating than trying to click a button that doesn’t do anything. When we design, we also need to design disabled, pressed, selected, and read-only states.
Research
Research Planning

Gathering research requirements
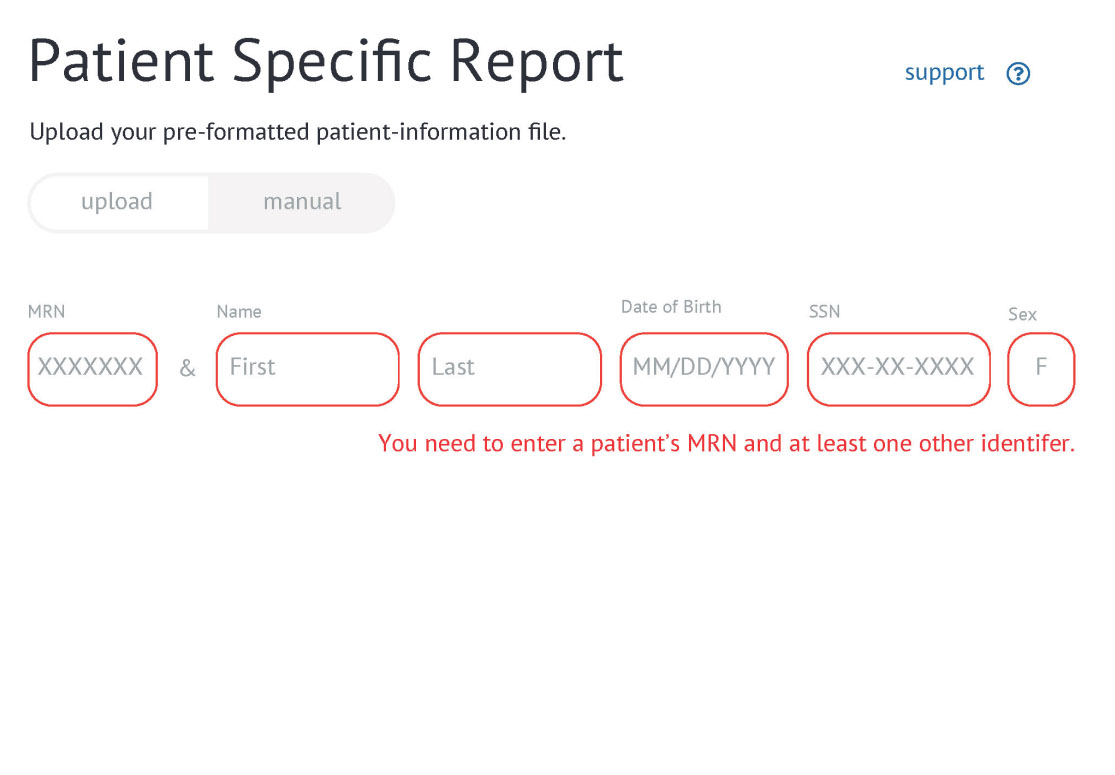
Research is a tool to test our assumptions. With immature design teams, these assumptions are often things I have to listen for or bring out on calls with stakeholders.

Writing test plans
My test plans include the questions we want answered by the study, recruitiing criteria and methods, and a detailed script.
Recruiting participants
For smaller user bases, I reach out to specific individuals based on connections. For larger user bases (for commercial products) recruitment platforms such as UserZoom, UserTesting, or Respondent.io are helpful.
Research
Research Activities
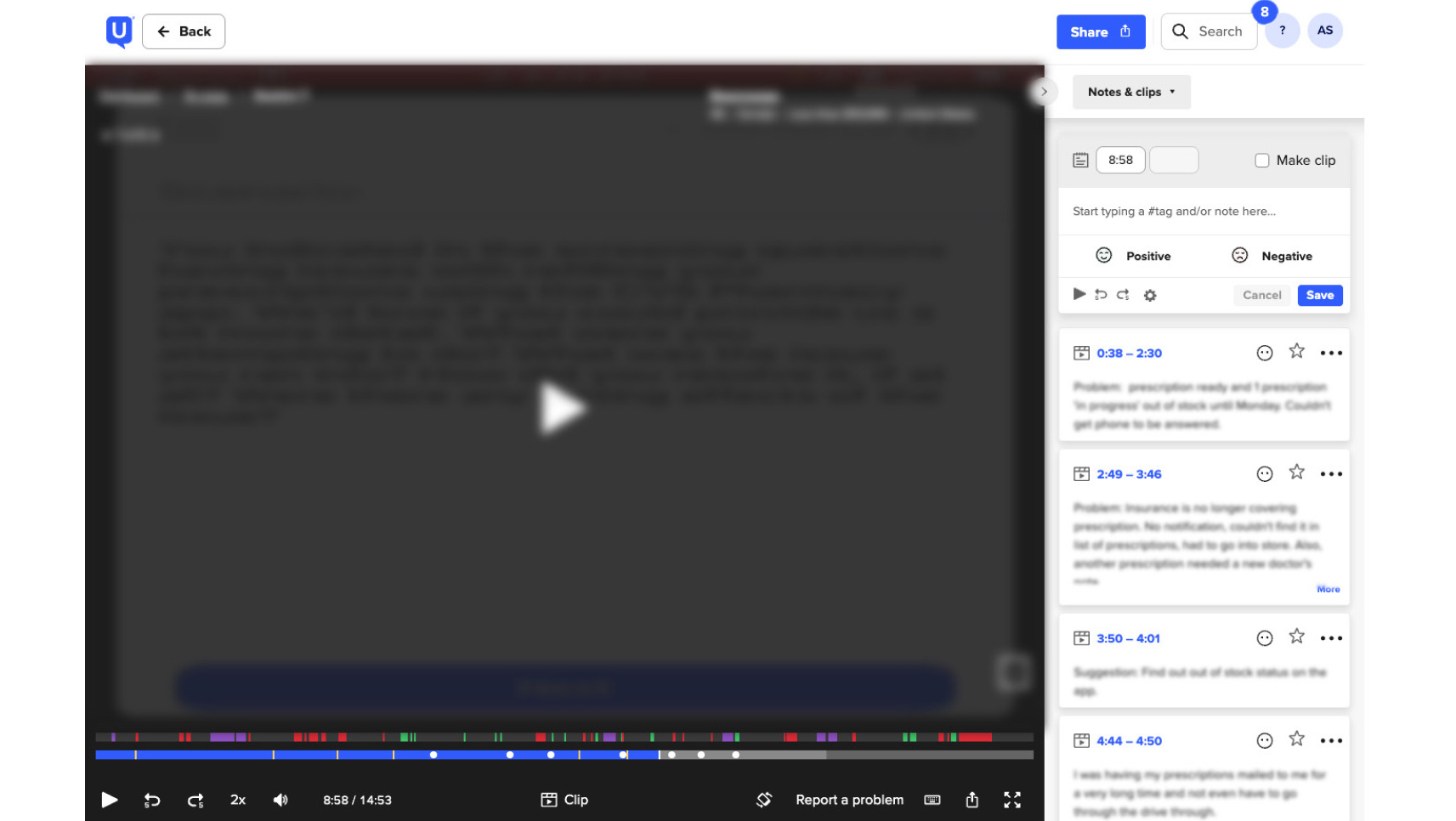
Usability Testing
While I much prefer guided usability tests as they can be both generative and evaluative forms of research, if I am lacking time and resources I will conduct unguided usability tests.
User Interviews
Early on in projects, or on projects that are more system-based than screen-based, user interviews can gather valuable insights around users’ attitudes, processes, or challenges.

Contextual Inquiries
Whenever I conduct usability testing, I prefer to do it in a user’s environment, on their device, with external factors available. This provides us the most accurate insights into real world scenarios.
Card Sorting
When approaching navigation projects, I use open card sorts to generate ideas on navigational categories and understand users’ associations and closed card sorts to confirm and refine our structure.
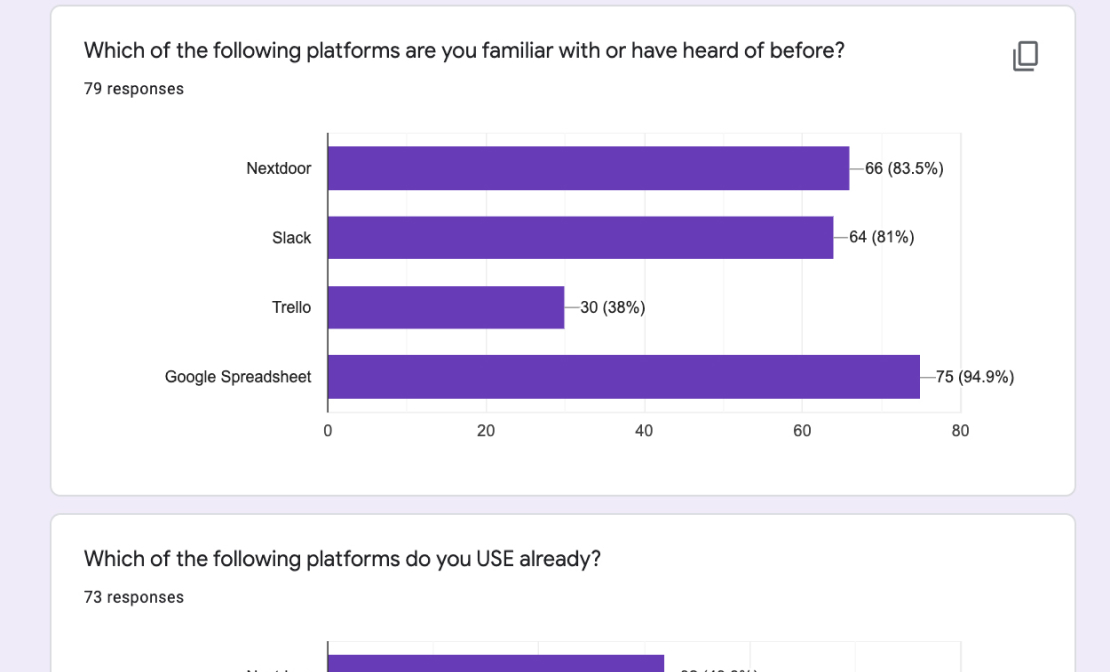
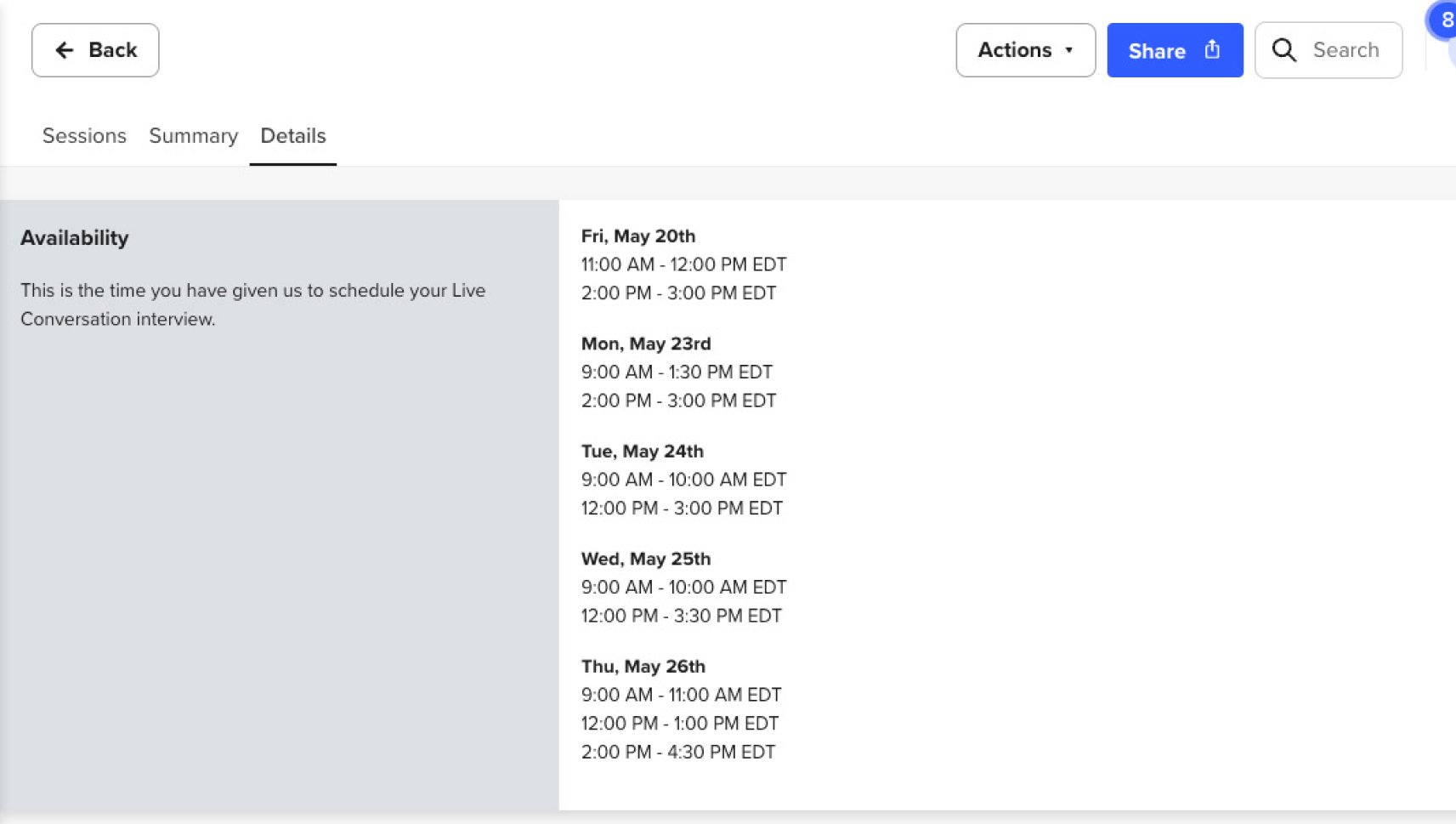
Surveys
I have used surveys to capture attitudinal feedback at an overall high level for a product or process.
Research
Research Analysis

Affinity Mapping
Affinity mapping is a team activity best done in person, but can also be done virtually in Miro or Figjam. The mapping creates organic groups of observations, quotes, or findings.
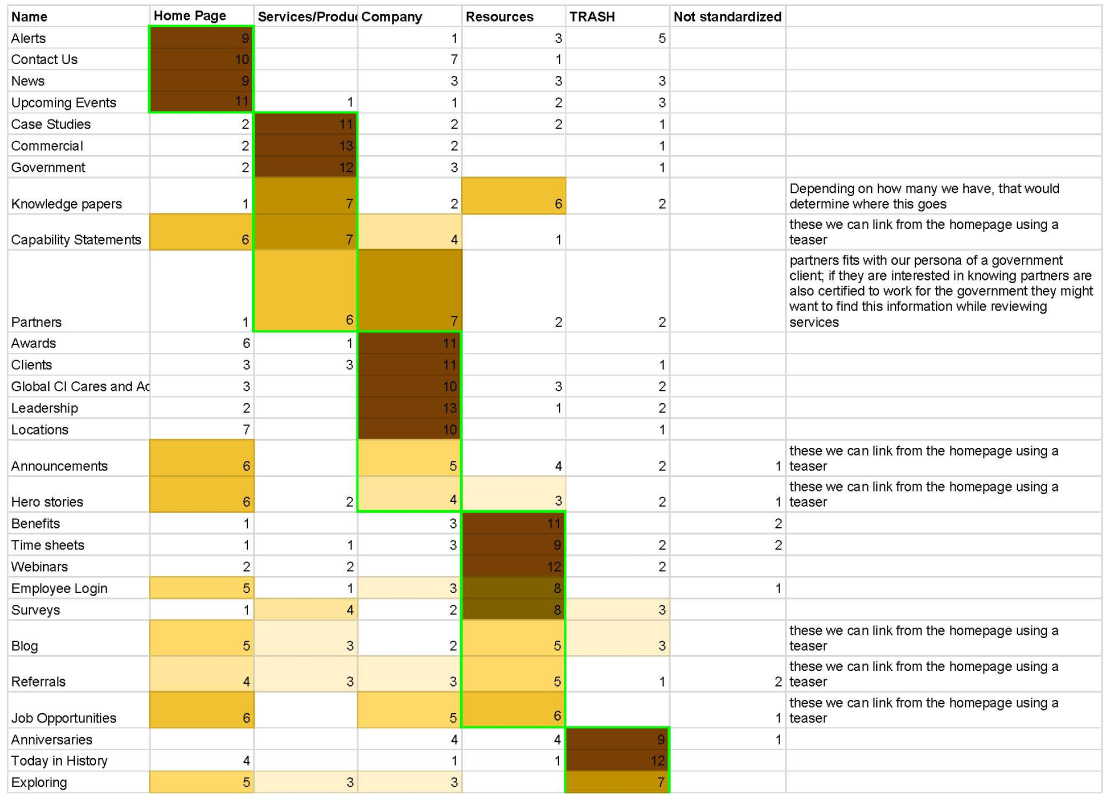
Card Sorting Analysis
Spreadsheets help organize quantitative results from a card sorting activity to determine trends of categories respondents made.
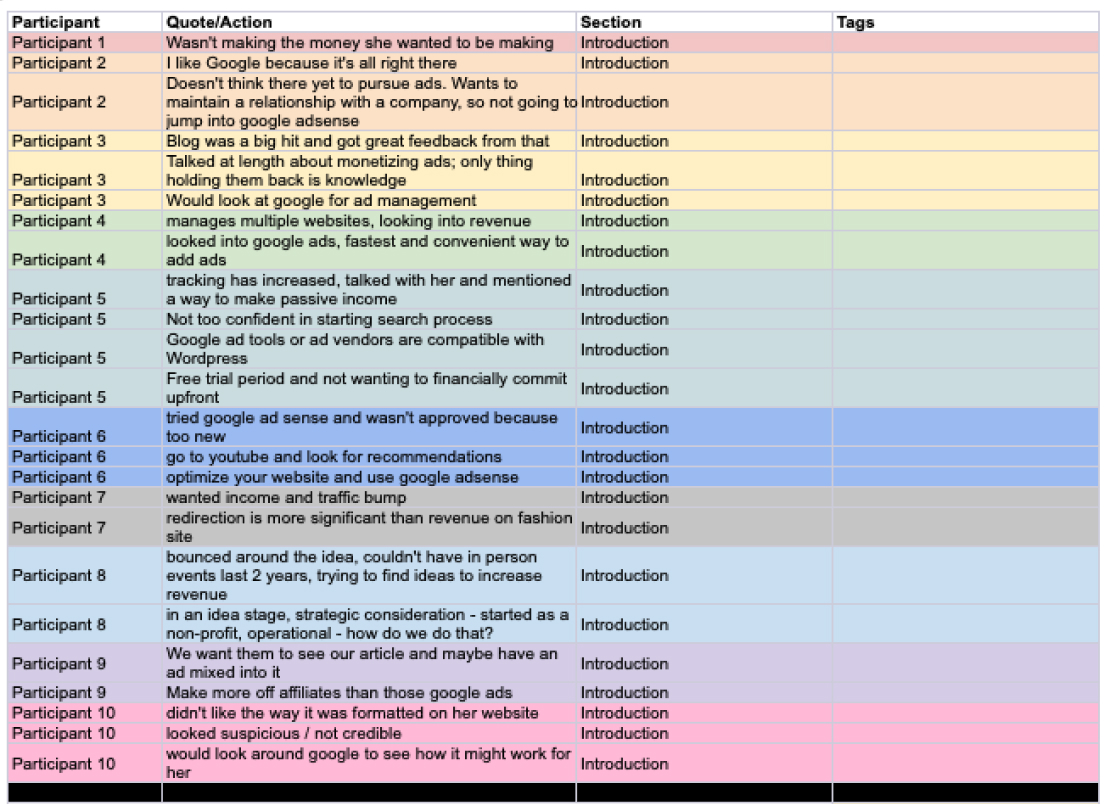
Research Coding
Research coding works best when testing abstract or large experiences that span multiple interfaces and invovle many user interviews. The codes can be assigned for sections of the experience, themes, common problem types, or even study questions.
Research
Research Deliverables
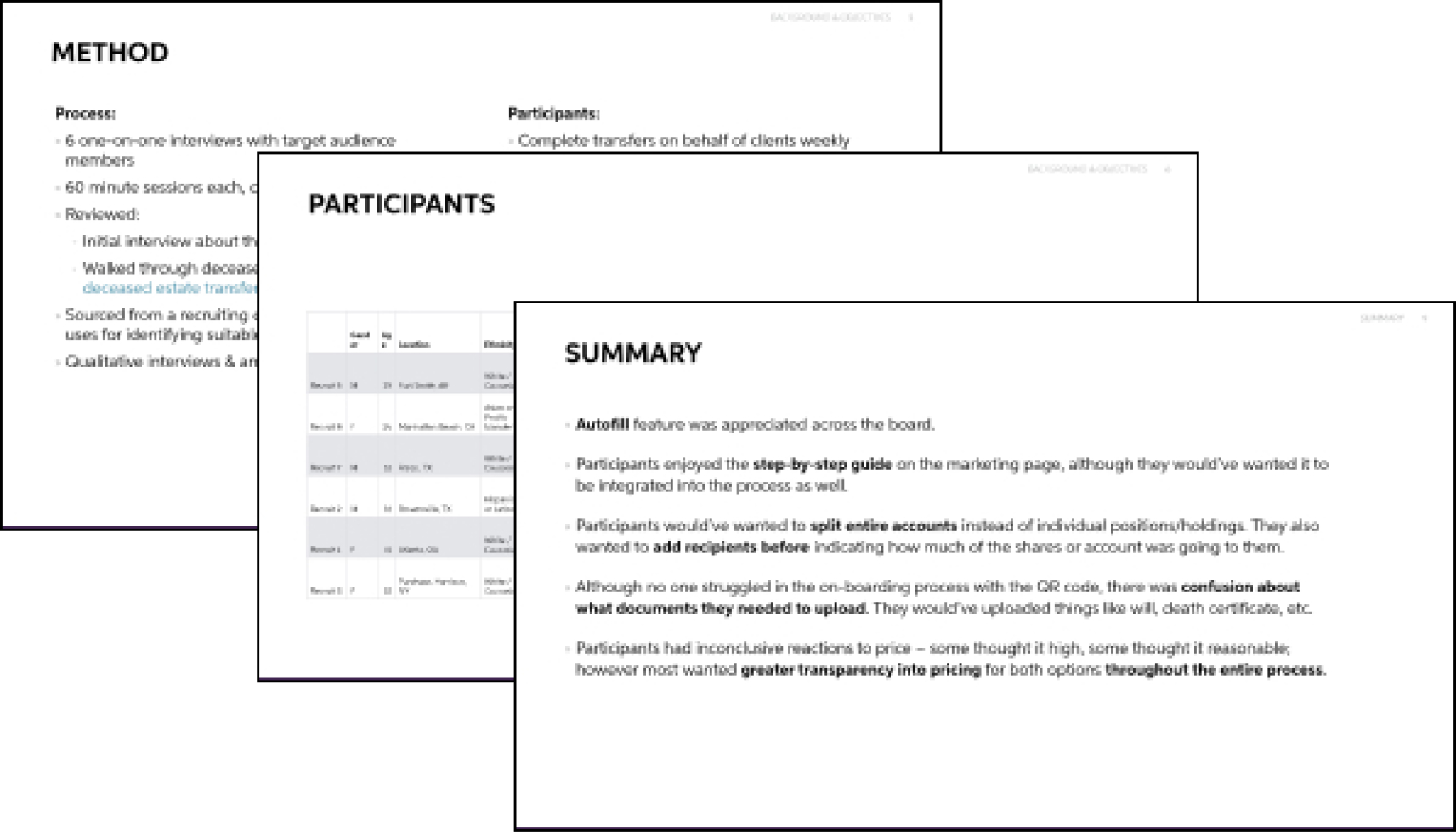
Formal Research Reports
The most important part of a research project is getting buy-in from the rest of the team; depending on the audience that may mean producing formal research reports, confluence pages, or conducting readouts.
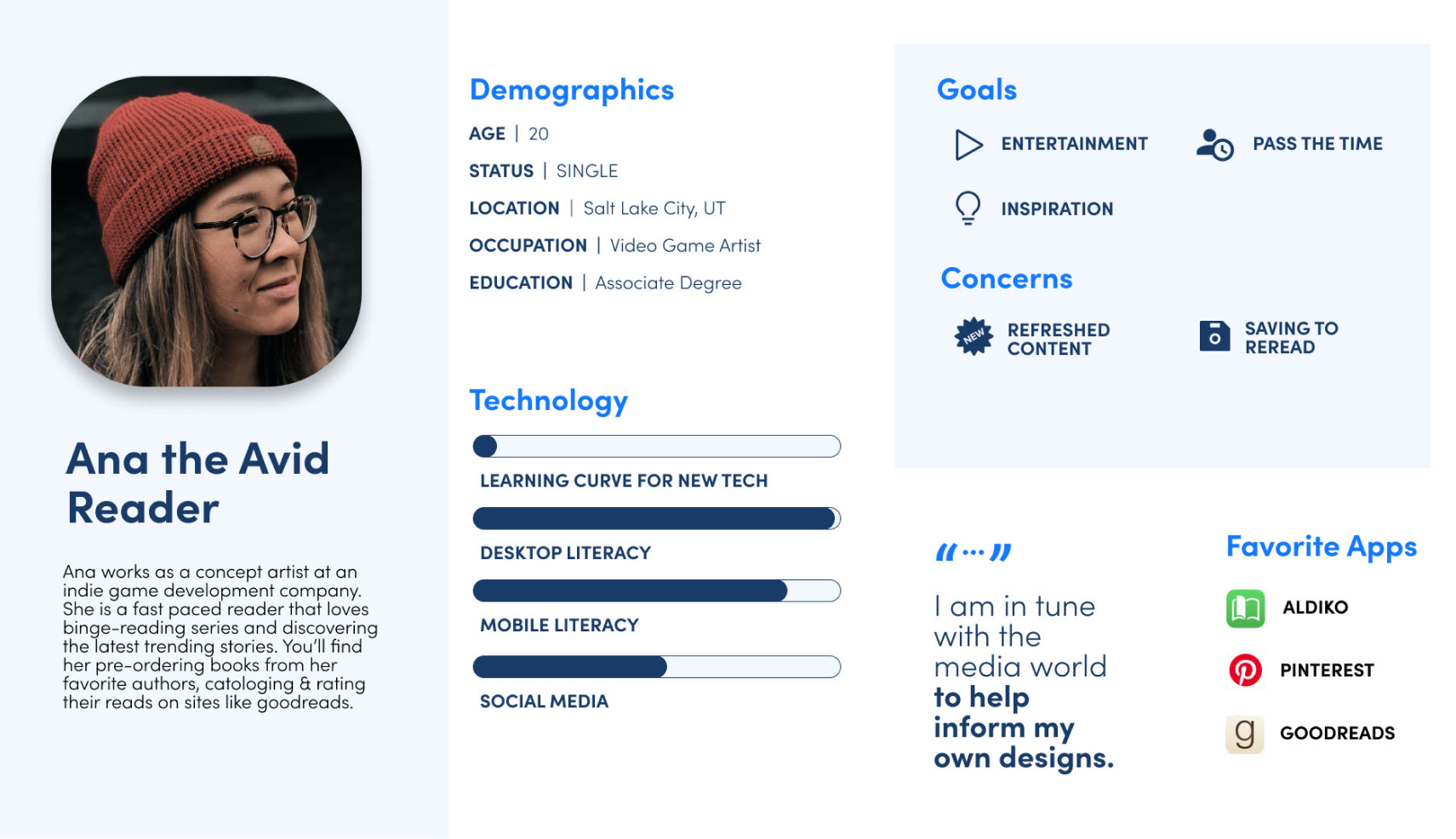
Personas
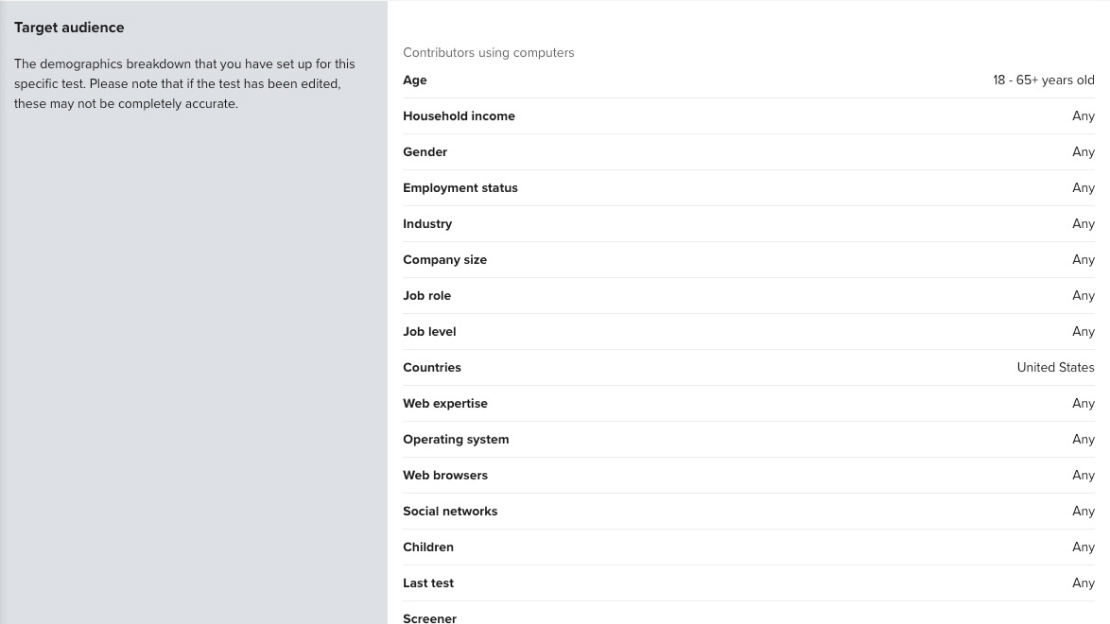
I will use personas usually for one of two reasons: to align stakeholders on our target audience and to recruit potential research participants. I find high-level personas are usually sufficient, but sometimes a more detailed ‘day in the life’ diary is needed to evoke empathy from the design team.
Strategy
Project Strategy & Service Design

Defining Product Terms and Language
When different departments own parts of an overall journey, it can be difficult to see the whole picture and understand where pain points arise. A bird's eye view map of the journey can bring light to these issues and inform siloed departments of the entire process.
Non-digital Prototyping
There are important non-digital aspects to every experience. The software I work on usually involves other APIs or plugins for authentication, mass email sending, or social sharing. While we can’t design these parts of the experience, they provide valuable context to include in prototypes.
Strategy
Defining Core Product Functionality
Something that is assumed, but rarely expressed aloud is the core flows of a product. Not only can UX bring to light differing assumptions, but it can help document a core functionality understanding for everyone.
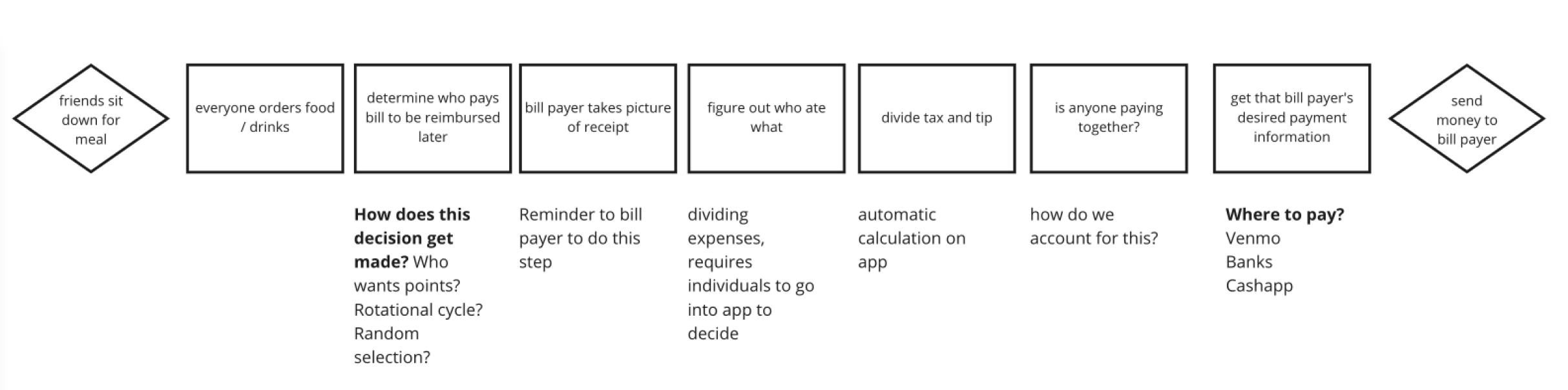
Strategy
Working within Existing Constraints
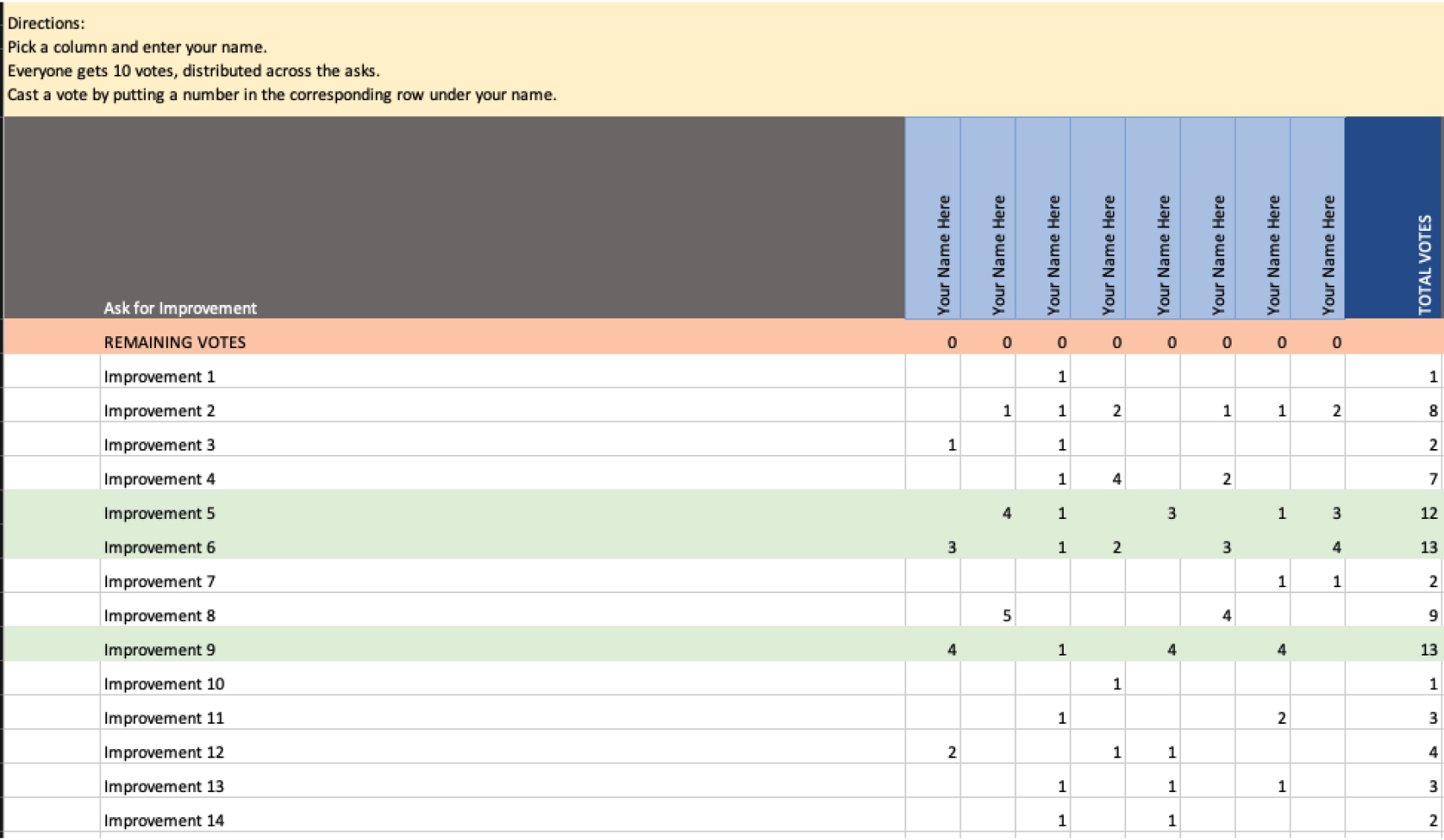
Designing around internal process constraints
Sometimes the best solution is changing a process entirely; however, not all organizations are ready to make that leap and departments often don’t have influence over what another department controls. In these cases, it is best to bring everyone together to prioritize changes or optimize around unchangeable parts of the process.

Designing around technical constraints
Is it better to build something custom or change the design to fit the constraints? This is a question I ask myself frequently. While designing custom things makes a product cutting edge and can better solve problems, it can come with increased build time, maintenance costs, and decreased predictability.
Site designed and coded by Me, Amelia Shuler.